Random on Random Vibration Tutorial
How to Run a Basic Random-on-Random Vibration Test on the Panther Control System
1. Safety First
• Random-on-Random testing introduces multiple overlapping random excitations—ensure all personnel are clear of the test area before applying drive signals.
• Inspect all transducers, cables, and mechanical fixtures for tightness and proper routing. Any loose hardware can lead to unsafe conditions or invalid data.
• Confirm the shaker and amplifier are rated for the combined spectral energy of both random signals.
• Verify accelerometer orientation and polarity. Use TEDS data to confirm sensitivity and identification.
• Ensure Abort, Stop, and Emergency Power Off (EPO) controls are clearly accessible at all times.
• Panther’s built-in safety system continuously monitors more than a dozen parameters up to 25 times per second, automatically aborting if any unsafe condition occurs.
2. System Setup
1. Power on the Panther system and amplifier, keeping the amplifier in standby mode until the test setup is verified.
2. Launch the Panther Random-on-Random application on the host PC.
3. If not already connected to the hardware, navigate via the Setup→ Set Input Type menu in the Panther software to establish hardware connection.
4. Verify that all input channels are active, calibrated, and within their voltage ranges. Panther’s automatic internal digital calibration (NIST referenced) ensures accurate operation.
5. Assign the proper output channel to the amplifier input and confirm signal polarity.
6. Use the Library to open a previous Random-on-Random setup or create a new one. Panther’s Library allows alias-based quick access without searching complex file paths.
3. Defining the Random-on-Random Test
1. In the Control tab, select the Random-on-Random test type.
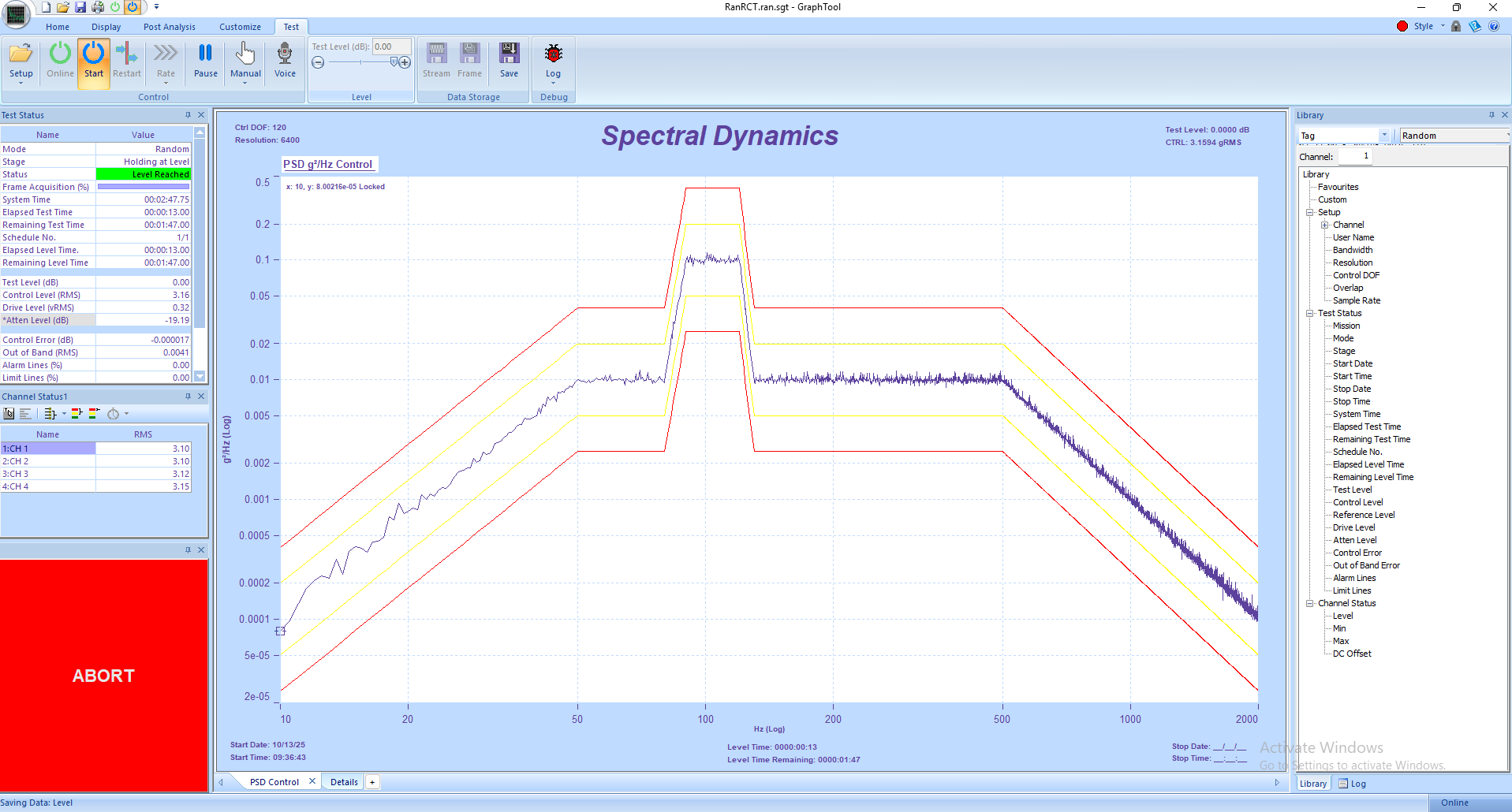
2. Define the base random spectrum by setting frequency range, overall level (g RMS), and spectral shape (PSD).
3. Add the modulated random profile. Define modulation bandwidth, depth, and update rate according to your test requirements.
4. Assign control and monitoring accelerometers. Verify channel sensitivity, units, and calibration constants.
5. Set control tolerances, warning, and abort limits. Panther performs a pre-test verification sequence to ensure safe operation before drive is applied.
6. Enable Adaptive Control to allow Panther’s dual-random digital filters to optimize both spectra simultaneously in real time.
7. Activate Multiple Acquisition Streams if different channels need distinct sample rates for detailed analysis.
4. Running the Test
1. Set the amplifier to ‘Operate’ mode once all pre-test safety verifications are complete.
2. Press Start in the GTX toolbar to begin the test. Panther performs an automatic self-check to confirm all limits, connections, and channels are valid.
3. During ramp-up, the system smoothly reaches target levels under adaptive equalization, maintaining safety and stability.
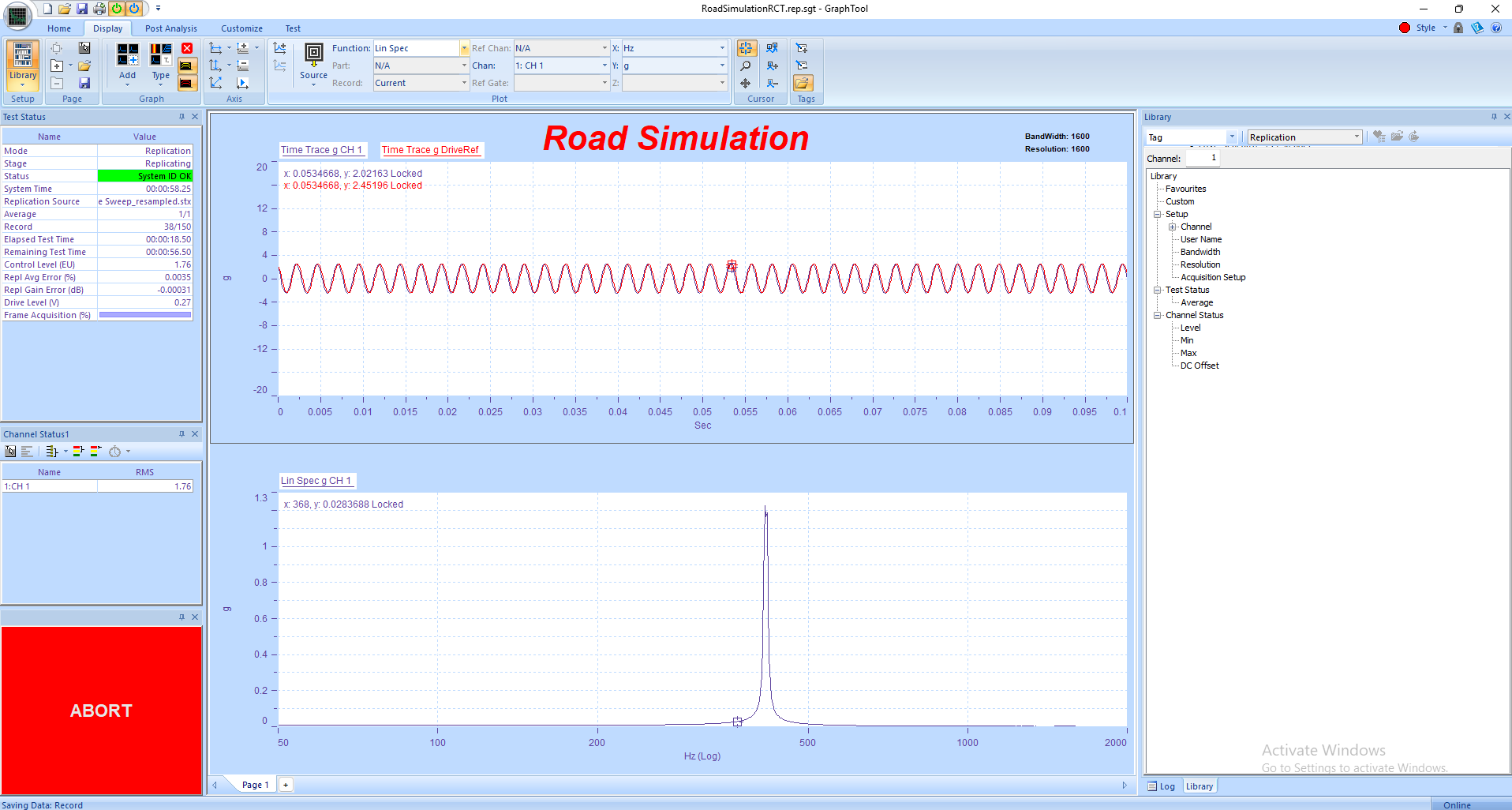
4. Monitor real-time PSD and time-domain plots in GTX. Use the Status Panels to view channel RMS levels, drive voltages, and safety warnings.
5. Panther’s adaptive algorithms continuously adjust both random excitations to maintain accurate control across the full frequency spectrum.
6. If any monitored parameter exceeds set limits, the system will automatically abort to protect the shaker and test article. The Abort button in GTX is always available for manual intervention.
5. Data Review and Reporting
• After test completion, Panther automatically saves all control, drive, and response data in the Library for future review.
• Use GraphtoolX (GTX) to analyze results — overlay live and historical runs, review PSDs for both random components, and compare control stability.
• Export results directly to Word, Excel, or PDF via the GTX Share function for documentation or reporting.
• Generate Composite and Waterfall plots to visualize how the modulated random spectrum evolves over time.
6. Panther Advantages in Random-on-Random Testing
• Safety-First Design: Monitors 12+ safety parameters 25 times per second to ensure full operator and equipment protection.
• Adaptive Dual-Random Control: Independent adaptive filters manage both base and modulated random spectra simultaneously, maintaining precise control across complex signal interactions.
• Ease of Use: Intuitive GTX interface and touch-screen compatibility simplify configuration, monitoring, and post-test analysis.
• High Performance: 24-bit ADCs, >110 dB dynamic range, and <1° phase match up to 100 kHz ensure accurate measurement and control.
• Real-Time Streaming: Continuous gap-free recording enables detailed review of transient or modulated behavior.
• Multiple Acquisition Streams: Capture data from various sensors at different sample rates for optimized resolution and storage efficiency.
7. Best Practices
• Perform a low-level pre-test to confirm proper system response and safety margins before applying full levels.
• Use Panther’s built-in verification to confirm all channels are operational and limits are properly configured.
• Regularly check accelerometer mounting torque and cable integrity for accurate data acquisition.
• Save your GTX layout and control setup as templates for consistency across multiple test campaigns.
• Back up calibration constants and Library files periodically to maintain traceable, repeatable results.