Resonance Search and Dwell Vibration Tutorial
How to Run a Basic Resonance Search and Dwell Vibration Test on the Panther Control System
1. Safety First
• Resonance Search and Dwell testing involves sweeping through natural frequencies and holding at resonant points — ensure all personnel are clear of the test area before applying drive signals.
• Inspect all mechanical fixturing, sensors, and cables to ensure secure connections. Loose components can create hazards and invalidate test data.
• Confirm the shaker and amplifier are rated for the full sweep range and dwell amplitude levels.
• Verify accelerometer polarity and grounding. Confirm TEDS identification and sensitivity for each input channel.
• Ensure Abort, Stop, and Emergency Power Off (EPO) switches are accessible and operational before beginning the test.
• Panther’s safety system monitors over a dozen parameters up to 25 times per second, automatically aborting if limits are exceeded to protect the shaker, DUT, and personnel.
2. System Setup
1. Power on the Panther system and the shaker amplifier, keeping the amplifier in standby until system verification is complete.
2. Launch the Panther Resonance Search and Dwell control application on the host computer.
3. If not already connected to the hardware, navigate via the Setup→ Set Input Type menu in the Panther software to establish hardware connection.
4. Verify that input channels are active, properly calibrated, and within expected ranges. Panther’s NIST-referenced digital calibration ensures traceable accuracy.
5. Select the output channel that drives the shaker amplifier input and confirm polarity and amplitude limits.
6. Use the Library feature to open a saved Resonance Search and Dwell setup or create a new one. Panther’s Library simplifies setup management and recall using alias-based file names.
3. Defining the Resonance Search and Dwell Test
1. In the Control tab, select the Resonance Search and Dwell (RSD) test type.
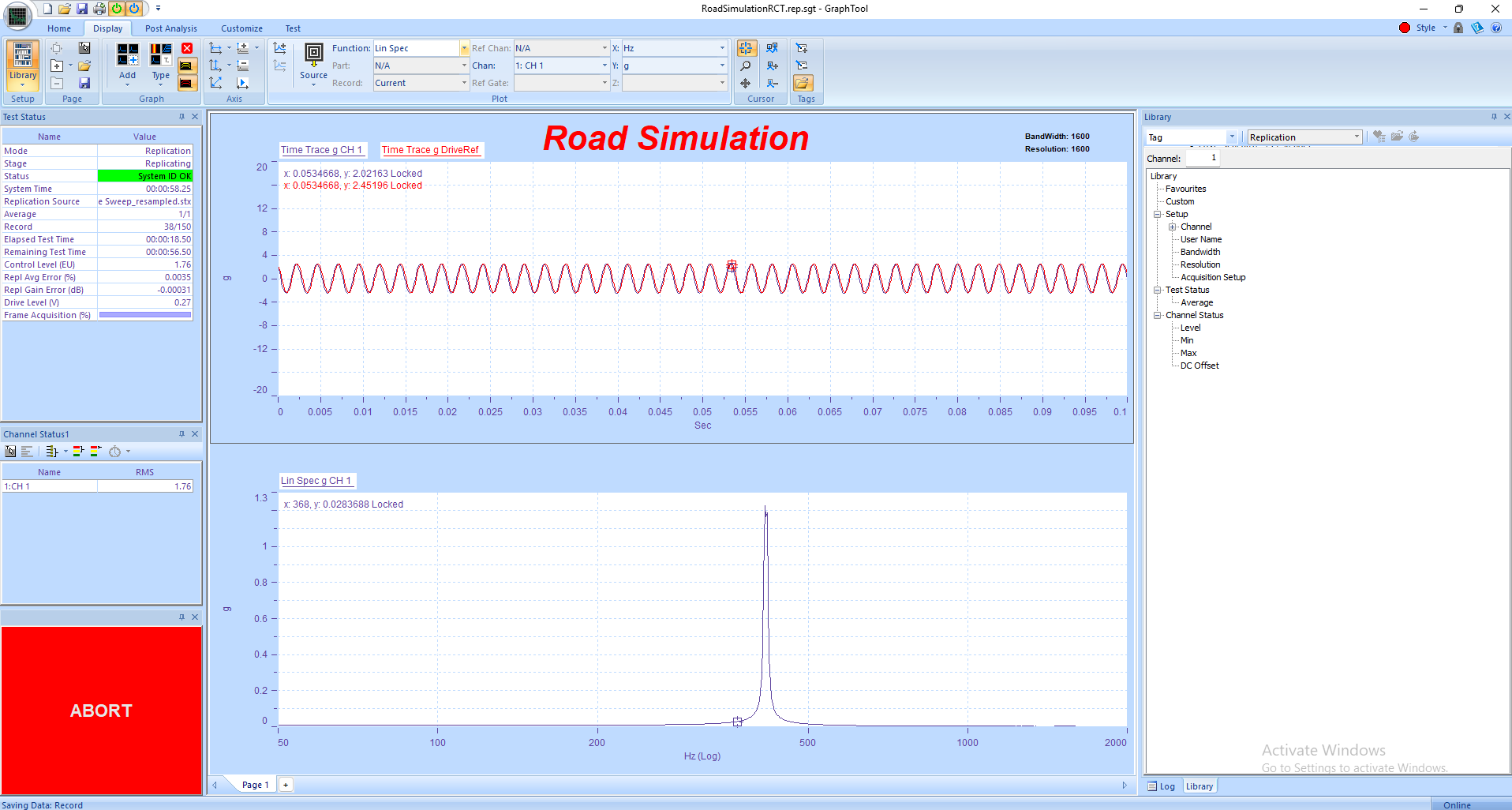
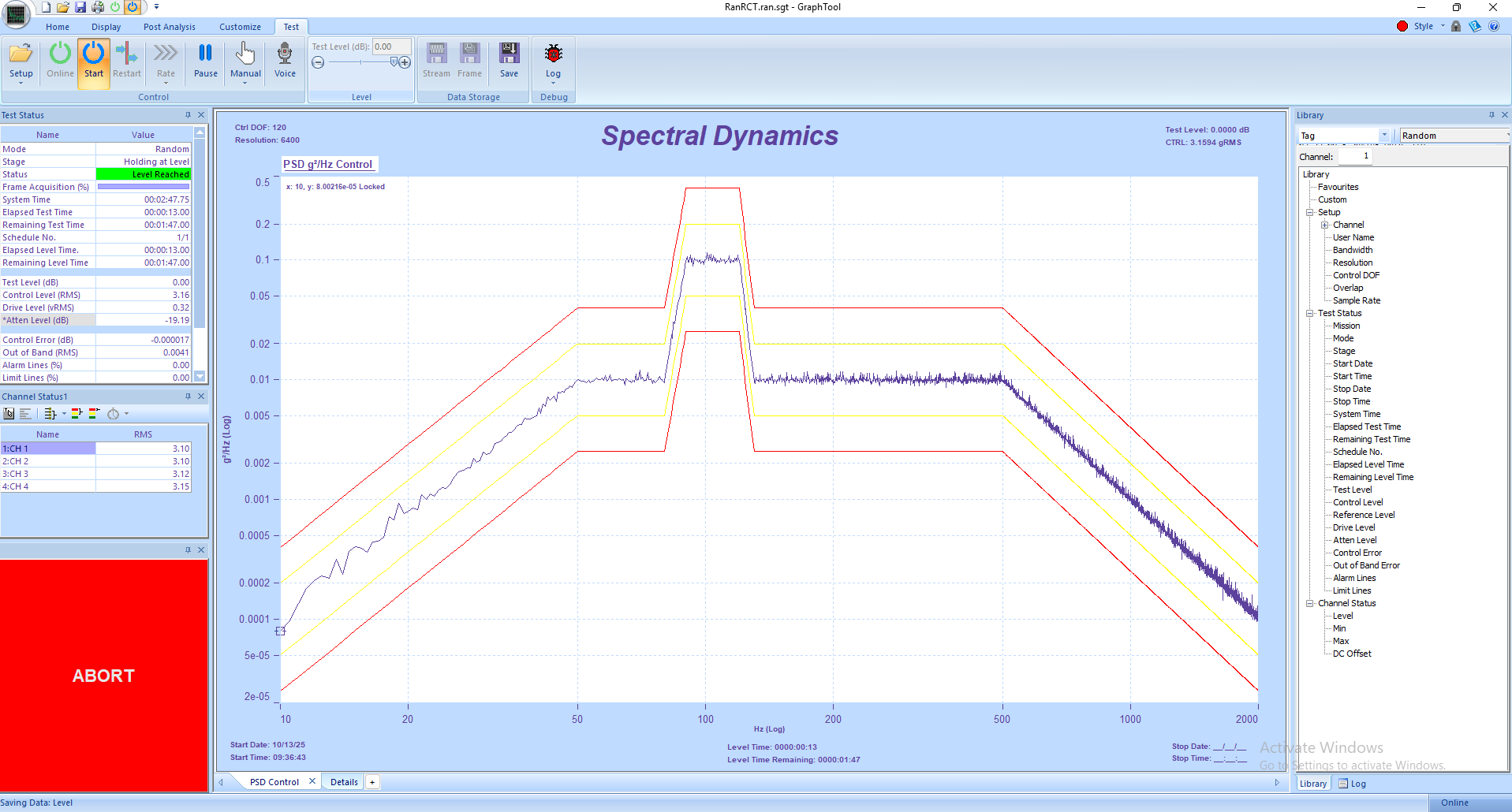
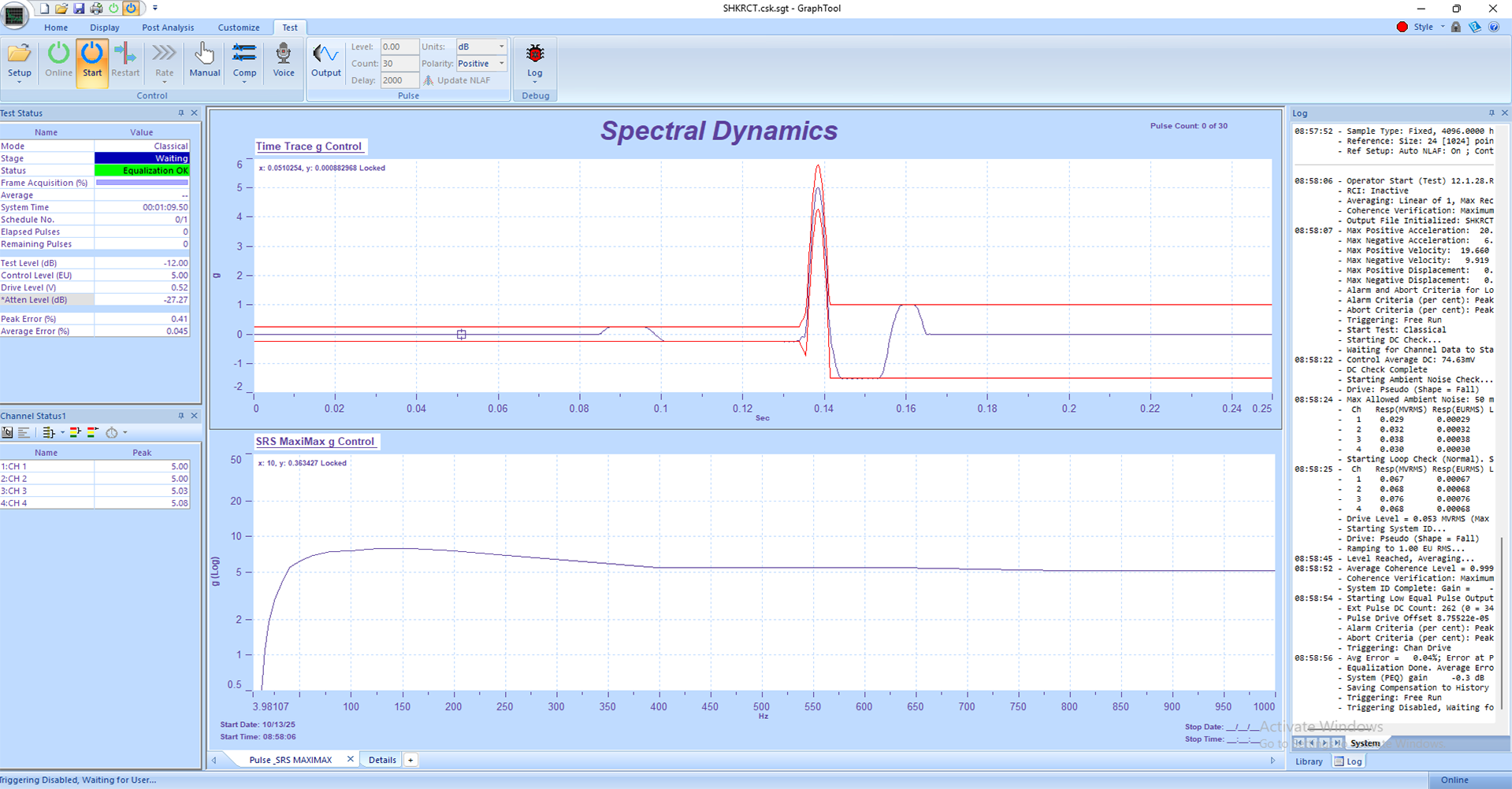
2. Define the sweep parameters, including start and stop frequencies, sweep rate, and control level (g RMS, g Peak, or displacement).
3. Assign control and monitor accelerometer channels, verifying their calibration and units.
4. Enable Tracking Filters to allow Panther to automatically identify resonant frequencies during the sweep. The system will precisely track phase and amplitude changes for accurate detection.
5. Set dwell criteria — either by amplitude (e.g., hold at a defined response level) or by time (e.g., dwell for a specified duration at each resonance).
6. Configure abort and warning limits for both drive and response channels. Panther’s real-time safety monitoring will automatically abort the test if any threshold is exceeded.
7. Enable Adaptive Control to optimize equalization in real time during the sweep and dwell segments for improved stability and accuracy.8. Save the setup once all parameters are verified.
4. Running the Test
1. Set the amplifier to ‘Operate’ mode after all pre-test checks are complete.
2. Press Start in the GTX toolbar to initiate the test. Panther performs a pre-test verification to ensure safe conditions.
3. The system sweeps through the defined frequency range under adaptive control, continuously monitoring for resonance peaks.
4. When a resonance is detected that meets dwell criteria, Panther automatically holds the drive frequency and amplitude at that point for the specified dwell duration.
5. Observe real-time plots of frequency response, control amplitude, and phase in GTX. Use the Status Panels to monitor RMS levels and safety indicators.
6. At the end of the dwell period, Panther resumes sweeping or completes the test sequence depending on setup parameters.
7. If any unsafe condition occurs, the system will automatically abort. The operator can also manually press the Abort button at any time for immediate stop.
5. Data Review and Reporting
• After completion, Panther automatically stores the control, response, and dwell data in the Library for easy retrieval.
• Use GraphtoolX (GTX) for analysis — view PSD plots, phase traces, and time histories to confirm resonance frequencies and dwell responses.
• Overlay multiple runs to compare resonance characteristics or repeatability across tests.
• Export results directly from GTX to Word, Excel, or PDF using the Share feature for reporting and documentation.
6. Panther Advantages in Resonance Search and Dwell Testing
• Safety-First Design: Panther continuously monitors critical parameters 25 times per second and automatically aborts in unsafe conditions.
• Adaptive Equalization: Automatically maintains stable control through resonant regions without overshoot or instability.
• Tracking Filters: Precisely identify and hold resonant frequencies using advanced phase-tracking algorithms.
• Ease of Use: GTX’s intuitive, touch-friendly interface simplifies setup, monitoring, and analysis.
• High Precision: 24-bit ADCs with >110 dB dynamic range and <1° phase match up to 100 kHz ensure accurate control and measurement.
• Real-Time Streaming: Gap-free data recording allows comprehensive post-test analysis and comparison across test runs.
• Library Integration: Instant access to prior RSD setups and results for efficient test management.
7. Best Practices
• Perform a low-level verification sweep before running the full test to confirm proper setup and safe operation.
• Use Panther’s pre-test check and abort limit setup to prevent excessive drive levels at resonance points.
• Ensure accelerometers are tightly mounted and located at key response points on the DUT for accurate resonance detection.
• Save GTX layouts and graph templates for consistent test visualization across operators and test programs.
• Back up calibration constants and Library data regularly to maintain test traceability and repeatability.